Syllabication: Rules, Division Patterns, & More
Posted by Brainspring on 15th May 2019
Our next Orton-Gillingham lesson basic covers decoding of multi-syllabic words and syllabication. We recently posted on how to address spelling dictation words using a multisensory approach.
What is Syllabication?
Syllabication exercises are a hallmark of multisensory phonics. Through these activities, students learn how to tackle unfamiliar multisyllabic words. Without this tool, comprehension can be significantly hindered for many students.
Why is Syllabication Important?
Imagine a struggling reader goes to read their assigned reading material and they come across a word such as this:
Constantinople
The student does his best to sound out the word but gets stuck on so many parts of the word. He then has trouble putting the chunks together and forgets where he even began with the word. He decides to skip the word, hoping the surrounding text can help him make meaning of what he reads. The quiz is tomorrow, he has a deadline and he must do well. Anxiety starts to build a little.
The student continues reading and comes across at least six more challenging words before he is done reading the page. His frustration is increasing, and his patience is decreasing. He attempts to take notes to outline the meaning of what he read and is at a loss. He cannot remember what he read because he was focusing so hard on even decoding the words on the page. He may give up at this point, become distracted, or let’s face it, bury his head in his book and take a nap.
The likely issue in this example is not that the student did not comprehend the material. Rather, he missed reading many of the words on the page and therefore could not gather the meaning. If someone read the page to this student, he more than likely would be able to better gauge the meaning and recap what the page was about.
The Impact of Syllabication in Reading
Syllabication is a step-by-step process that slows down the rapid process used by efficient readers and breaks down the steps for struggling readers. By breaking a word into small, manageable syllables, identifying the vowel sounds in the syllable, and sounding out a word syllable by syllable, the reader can decode (read) the word using syllabication.
Readers who cannot apply the syllabication process to more complex words become less efficient readers as material becomes more challenging, eventually compromising their ability to comprehend higher-level reading material.
To integrate syllabication into reading, you could have students scan the paragraph and identify any words that they cannot decode. Next, walk them through the process of syllabicating those difficult words. At this point, it might be necessary for you to also define these words. Now, the student is ready to read the paragraph.
Rules of Syllabication
Understanding syllable division rules helps students decode unfamiliar words and apply consistent spelling patterns. The English language follows several key syllabication rules that guide how words are divided. Here are the main rules:
- Every syllable must have at least one vowel sound – A syllable cannot exist without a vowel, as vowels are the foundation of spoken syllables.
- V/CV Pattern – When a single consonant appears between two vowels, it typically goes with the second syllable (ex: ti-ger, pa-per).
- VC/V Pattern (Rabbit Rule) – When two consonants are between vowels, they often split, placing the first consonant with the first syllable (ex: rab-bit, nap-kin).
- Keep digraphs and blends together – Letter combinations that form a single sound (digraphs like sh, th, ch) or consonant blends (like bl, str) should not be separated when breaking words into syllables (ex: push-ing, con-struc-tion).
- Prefixes and suffixes stay intact – When dividing words with affixes, keep prefixes and suffixes as whole units (ex: re-play, un-happy, help-less).
- Silent E stays with the preceding syllable – Words following the vowel-consonant-e pattern keep the final silent e in the first syllable (ex: cake, hope-ful).
- Consonant-le forms a separate syllable – When a word ends in a consonant-le pattern, it forms its own syllable (ex: ta-ble, puz-zle, mid-dle).
Syllabication Types
If students learn how to break apart words based on their division pattern and explicitly learn the rules of each syllable type, they will have success in reading a large chunk of the words in this very unfamiliar English language.
Syllable types found in English:
- Closed: a short vowel sound with a consonant after the vowel.
- Open: a long vowel sound with a single vowel and no consonant after the vowel.
- Silent -e: a silent vowel that jumps over the one consonant and makes the single vowel say its own name.
- Consonant-le: a syllable that does not contain a sounded vowel (the e is silent, but when the syllable is pronounced there is a distinct schwa sound before the l.
- Vowel Teams: Two vowels that work together to make a long vowel sound.
- Bossy-R: A vowel-consonant pair also called R-controlled because the r controls and obscures the sound of the vowel immediately preceding it. The vowel does not make a long or short sound.
- Diphthong: a pair of vowels making a new sound, neither long nor short.
- Schwa: Syllable that occurs in an unstressed, unaccented syllable. The vowel (often but not exclusively the a) makes the short u sound when the word is pronounced.
Teaching Syllable Division
When a student reaches an unfamiliar multisyllabic word, have them try the following steps to break the word down. It is important to follow these steps in the order listed below:
- Underline and label the first two vowels
- Draw a bridge to connect the vowels
- Label the consonants on the bridge
- Divide using the pattern
- Identify the syllable types *
- Read syllables
- Read word
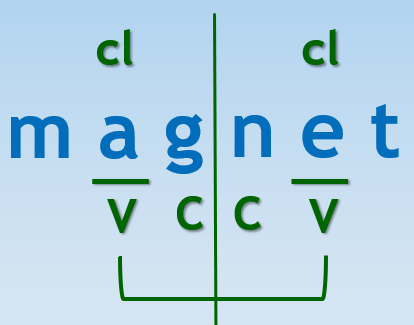
* In this case, mag and net are both closed syllables (labeled with a CL for closed).

Empower Your Students: Syllabication Activities
Students grasp the rhythm and structure of words through skillful syllabication instruction. By breaking down complex words into manageable parts, learners can confidently navigate reading and pronunciation challenges. Educators hold the key to this crucial aspect of literacy with a range of instructional strategies designed to foster understanding and retention.
Diverse Teaching Techniques to Enhance Syllabications Skills
Embracing variety, instructors can introduce syllabication through multisensory experiences. Visual cues, auditory exercises, and tactile activities ensure a multi-faceted approach that caters to different learning styles. For instance, colorful posters displaying syllable division rules serve as quick visual references for students, while clapping hands to the beat of syllables in words sharpens auditory analysis.
Complementing the traditional approaches, digital tools can present syllabication in interactive and appealing formats. Online applications offering syllable segmentation exercises enable students to practice independently, receiving immediate feedback that underscores their progress.
Educational Games for Syllable Recognition
Marrying instruction with entertainment, educational games can transform the learning of syllables from a mundane task to an exhilarating challenge. Incorporating board games that entail dividing words into syllables, or computer games where students navigate syllable-based puzzles, can significantly pique the interest of learners and sharpen their skills simultaneously.
- Syllable Bingo: Featuring a twist to the classic game, syllable bingo requires students to recognize the number of syllables in words to win, fostering their ability to decode words rapidly.
- Syllable Sort: Syllable Sort has students categorize words based on syllable count in small groups. This instills a sense of teamwork and enhances students’ syllabic understanding
Face-to-face or digital, incorporating games into the syllabication curriculum not only reignites student engagement but also allows for the iteration of syllable concepts within a relaxed environment. The seamless blend of focused learning objectives with the intrinsic motivation provided by gameplay secures a memorable educational experience.
More Syllabication Resources
- Multisensory Monday: Thumbprint Syllabication
- Multisensory Monday: Beginning Syllabication for Struggling Students
- Multisensory Monday: Syllabication Home Run
- Multisensory Monday: Syllabication Word Uno
- Multisensory Monday: Snowball Syllabication
- Multisensory Monday: File Folder Syllabication Game
For further helpful hints, click HERE to watch one of our videos on syllabication!
Written by Brainspring



